The working principle and advantages of reverse osmosis water treatment!
Views: 7337
Author: Site Editor
Origin: Site
The working principle and advantages of reverse osmosis water treatment!
Reverse osmosis is a membrane separation technique that uses pressure as a driving force by selecting a function of permeating (semi-transmissive) membrane. When the pressure applied in the system is greater than the osmotic pressure of the aqueous solution, the water molecules continuously permeate the membrane. The impurities flowing into the central tube through the product water channel and then flowing out of the water at one end, such as ions, organic matter, bacteria, viruses, etc., are trapped on the inlet side of the membrane, and then flow out at the outlet end of the concentrated water, thereby achieving the purpose of separation and purification.
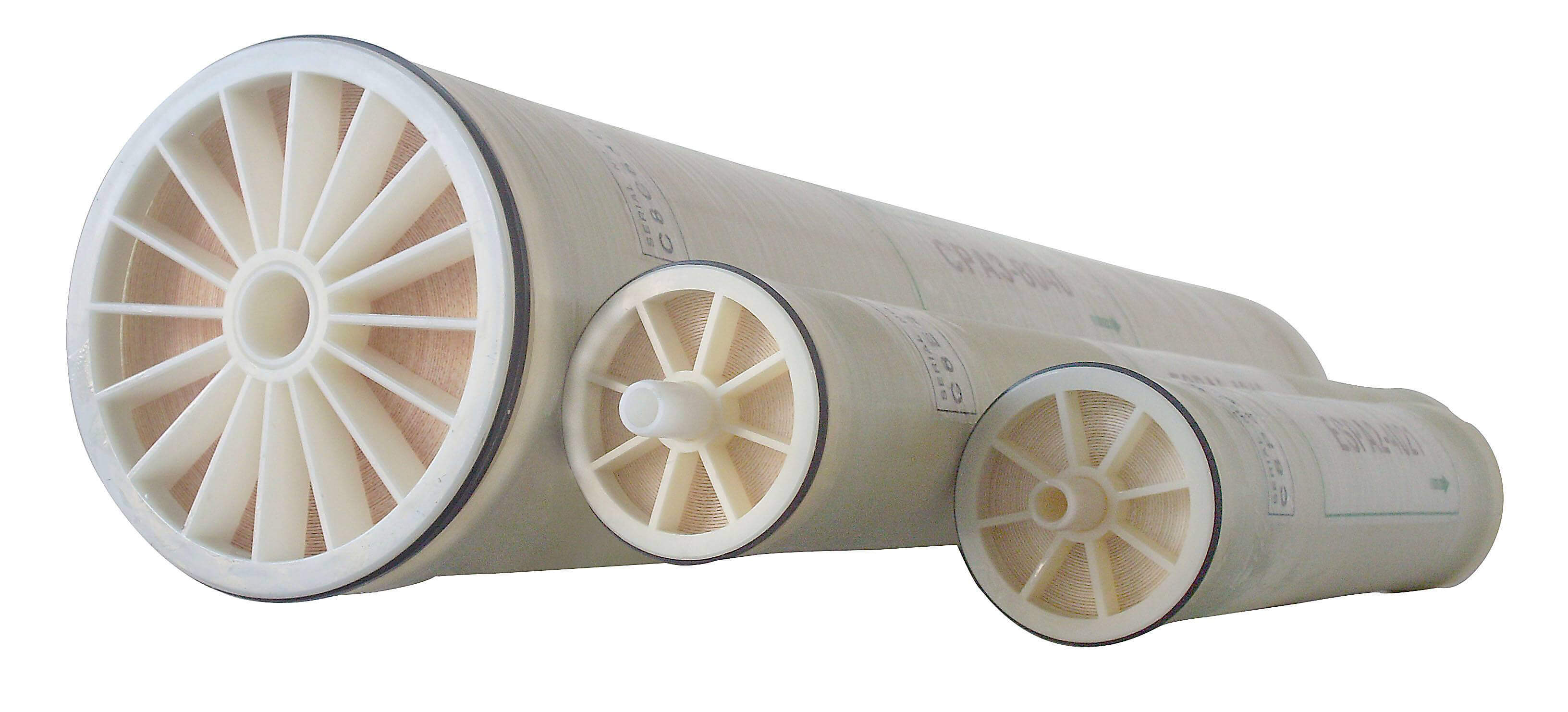
Reverse osmosis is a membrane separation technique that uses pressure as a driving force by selecting a function of permeating (semi-transmissive) membrane. When the pressure applied in the system is greater than the osmotic pressure of the aqueous solution, the water molecules continuously permeate the membrane. The impurities flowing into the central tube through the product water channel and then flowing out of the water at one end, such as ions, organic matter, bacteria, viruses, etc., are trapped on the inlet side of the membrane, and then flow out at the outlet end of the concentrated water, thereby achieving the purpose of separation and purification.
Reverse osmosis technology is commonly used in fresh water of seawater and brackish water; softening treatment of water; wastewater treatment and purification, concentration and separation of food, pharmaceutical industry and chemical industry.
In addition, the reverse osmosis technology has also achieved good results in the pre-salting treatment, which can reduce the load of the ion exchange resin by more than 90%, and the amount of the regenerant of the resin can also be reduced by 90%. Therefore, it not only saves money, but also contributes to environmental protection. Reverse osmosis technology can also be used for particles, organic substances and colloids in water, which has a good effect on reducing the pollution of ion exchange resin and prolonging the service life.
Reverse osmosis is one of the most widely used desalination technologies in the preparation of high-purity water. It is isolated in the range of ions in the solution and organic matter with a molecular weight of several hundred, reverse osmosis (RO), ultrafiltration (UF), microporous membrane filtration ( Both MF) and electrodialysis (ED) technologies are membrane separation techniques.
In the past 30 years, reverse osmosis, electrodialysis, ultrafiltration and membrane filtration have entered industrial applications and have developed rapidly. In semiconductors, integrated circuit manufacturing processes, food and pharmaceutical industries, reverse osmosis is often used as desalting in the preparation of high purity water. Ultrafiltration is often used as a post-treatment for water systems, and membrane filtration is used for pretreatment and post-treatment of water treatments to filter particulates and bacteria.
working principle:
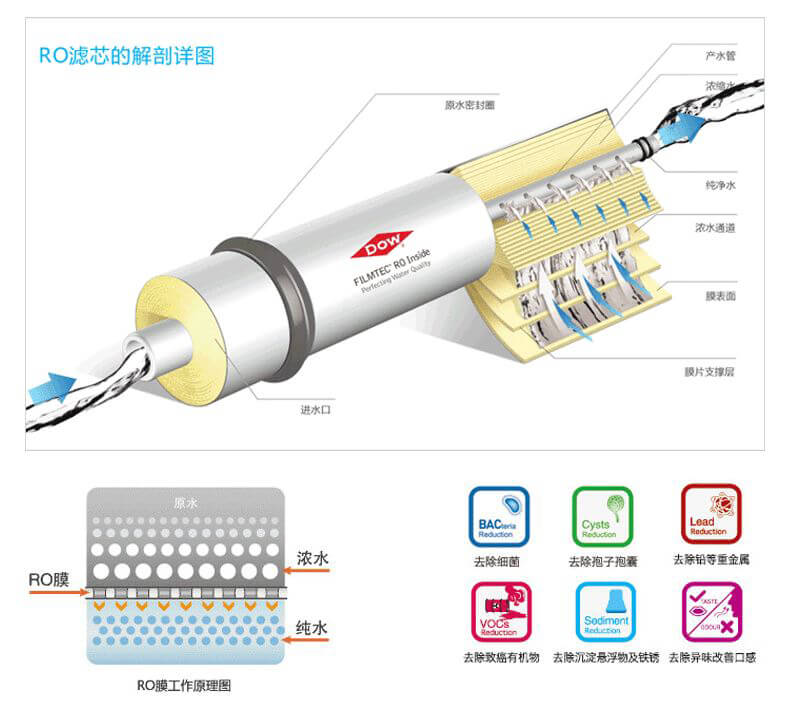
The system desalination rate of reverse osmosis equipment is generally 98-99%. Such salt removal rate can meet the requirements in most cases. In the electronics industry, ultra-high pressure boiler feed water, individual pharmaceutical industry requirements for pure water May be higher. At this point, the single-stage reverse osmosis equipment cannot meet the requirements.
Penetration is common in nature. For example, when a cucumber is placed in salt water, the cucumber will become smaller due to water loss. The process by which water molecules in cucumber enter the brine solution is the infiltration process. If a water tank is used to penetrate a pool, the water pool is divided into two parts, and pure water and brine are injected into the same height on both sides of the diaphragm. After a while, it can be found that the pure water level is lowered, and the liquid level of the brine is raised. The phenomenon in which water molecules migrate through the membrane into the brine is called infiltration. The rise in salt water is not endless, reaching a point of equilibrium at a certain height. At this time, the pressure represented by the liquid level difference at both ends of the diaphragm is called the osmotic pressure. The magnitude of the osmotic pressure is directly related to the concentration of the brine.
After the above device reaches equilibrium, if a certain pressure is applied to the liquid surface of the brine end, the water molecules will migrate from the brine end to the pure water end. The phenomenon that the liquid molecules migrate from a dilute solution to a concentrated solution under pressure is called a reverse osmosis phenomenon.
If brine is added to one end of the above facility and a pressure above the osmotic pressure of the brine is applied at that end, we can get pure water at the other end. This is the principle of reverse osmosis water purification.
The key reverse osmosis water production facility, there are two, one is a selective membrane, we call semi-permeable membrane, the second is a certain pressure.
Briefly, reverse osmosis semipermeable membrane has many holes, the size of water molecules with the size of the holes considerably, due to bacterial, viral, and most of the organic pollutants in water molecules is much larger than hydrated ions, and therefore can not penetrate reverse osmosis, semi-permeable membrane and is separated from the aqueous permeable reverse osmosis membrane.
Among the many kinds of impurities in water, soluble salts are the most difficult to remove. Therefore, the water purification effect of reverse osmosis is often determined according to the high and low salt removal rate. The reverse osmosis rate is mainly determined by the reverse osmosis semipermeable membrane. selectivity. At present, the salt removal rate of the highly selective reverse osmosis membrane element can be as high as 99.7%.

